The following headlines link to summaries of research published in past years. Using the filters in the navigation bar, you can filter the summaries by research area, disease or lab group.
-

Pregnancy Health, from Bench to Bedside
ISB is leading a comprehensive clinical study to tease out the intricacies of pregnancy as it progresses from conception to postpartum. In collaboration with Magee-Womens Health, ISB is collecting an exhaustive set of maternal and fetal health parameters — digital health, physiological, behavioral/contextual, molecular, clinical, and medical imaging measures — from multiple modalities and over the course of gestation.
-

Placenta and Preterm Birth
ISB is using systems biology to map molecular network dynamics in normal pregnancy, as well as study changes that occur in pregnancies with complications such as preterm birth. By using a systems approach, we hope to gain a more comprehensive understanding of pathological changes that occur in pregnancy, and identify women most at risk of developing pregnancy complications.
-
Mapping the early effects of the Huntington’s disease mutation in mice
3 Bullets: A multi-institute collaboration mapped in high resolution the earliest effects of the Huntington’s disease mutation in mice The study included four different genetic strains of mice which allowed the researchers to observe differences in the rate of mutation-induced changes as a result of genetic background Mapping early HD pathogenesis expands our understanding of early disease transitions and will inform other studies on proximal mechanisms and how to slow…
-
An Integrated Systems Approach to the Development of Molecular Signature of Biological Relevance for Glioblastoma
Code (ipython notebooks), html files, data and figures for review of the analysis done for An Integrated Systems Approach to the Development of Molecular Signature of Biological Relevance for Glioblastoma are available for download from GBM-blood-markers-paper.zip [7.6 MB]. The zip files contain data, figures and html output from ipython notebooks as well as the original runnable notebooks. The ipython notebooks to allow reproduction of results from statistical analysis detailed in An…
-
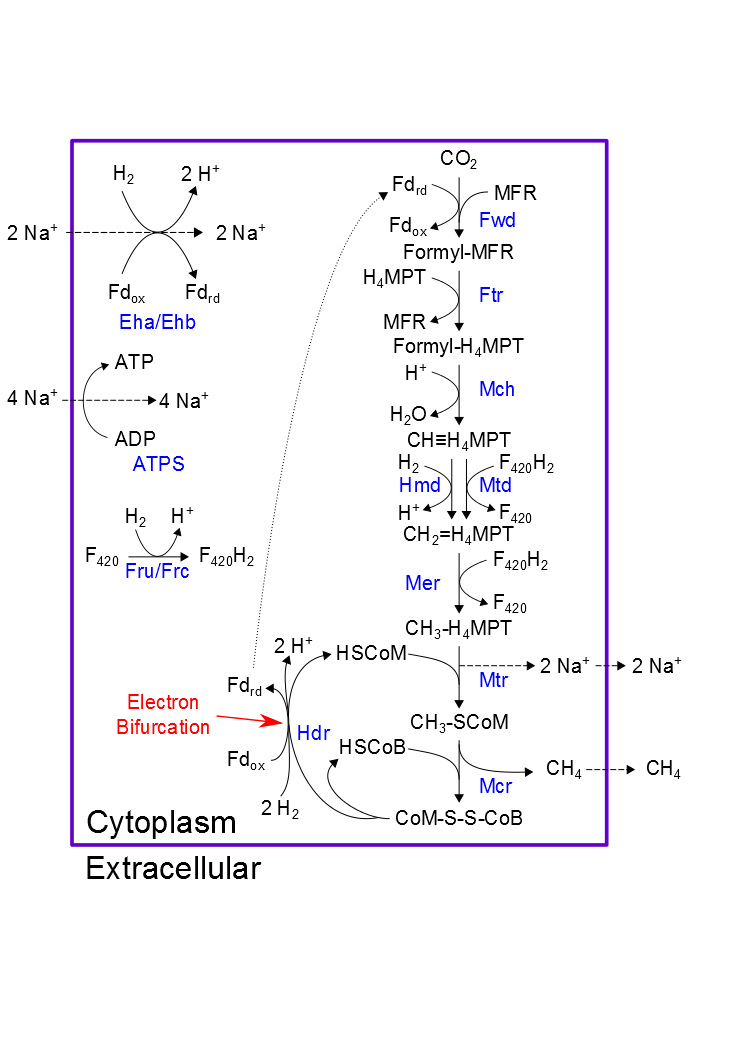
Methanococcus maripaludis reconstruction
Methanococcus maripaludis is an archaeon capable of generating methane gas from carbon dioxide and hydrogen. We have reconstructed its metabolism to enable better understanding of methanogenesis, particularly for learning ways to harness the process for producing liquid fuels from methane. Data and Software Files: Project on GitHub
-

Comparative analysis of yeast metabolic network models
Scientists have been mapping the chemical reactions cells use to grow and manage waste since before enzymes were first identified more than 150 years ago. The model yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has one of the most extensively studied metabolic networks, including at least 25 metabolic network models published since 2003. If iterative model improvement refines the metabolic network map, we would expect eventual convergence to a full, accurate metabolic network reconstruction….
-
Molecular Signatures of Disease
Molecular Signatures of Disease Disease Classification based on high-throughput expression data With the goal of developing novel methods for disease classification, we have implemented the relative expression classification algorithms, top-scoring pair (TSP) and top-scoring triplet (TST), for the graphics processing unit (GPU). The GPU is a specialized hardware most commonly associated with gaming applications. However, with the NVIDIA’s release of the Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA), the GPU became a…
-
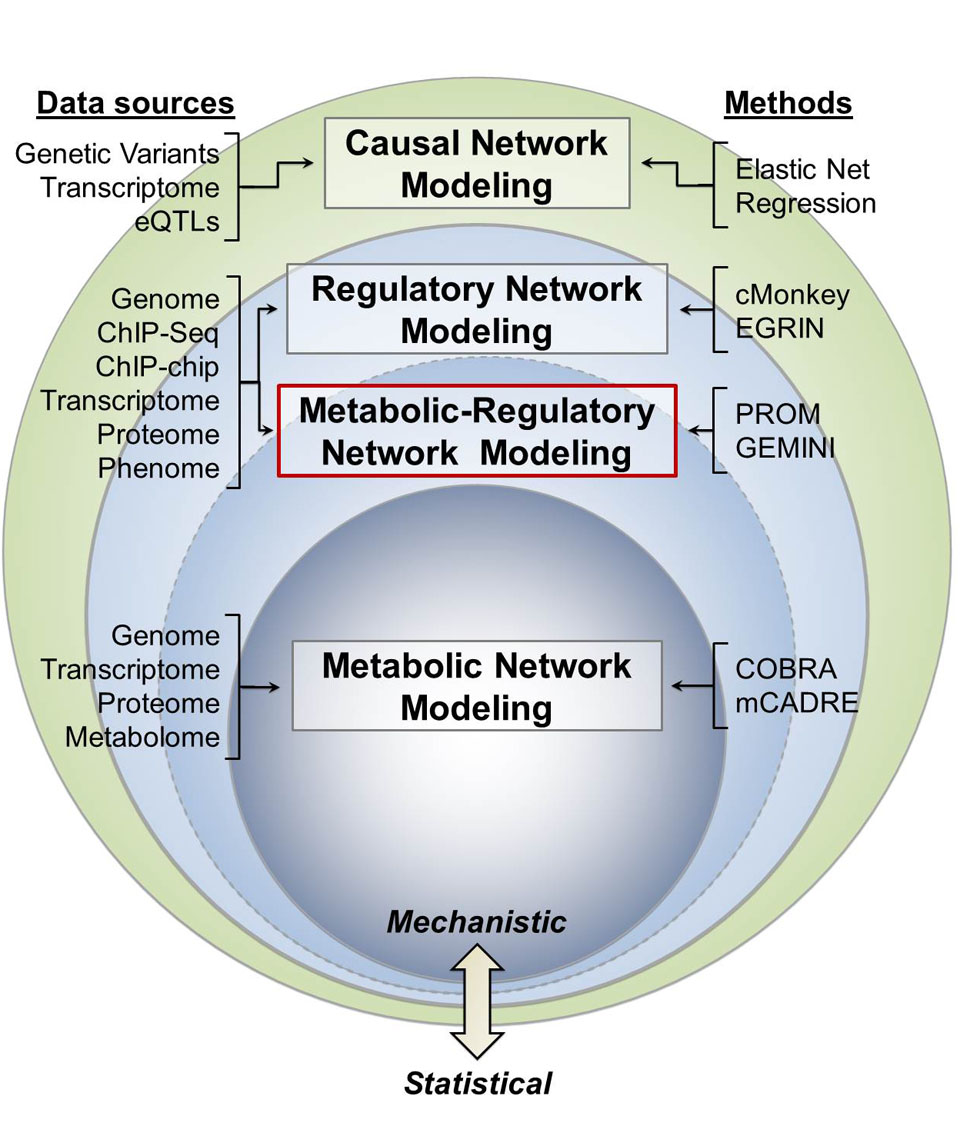
Integrated Network Modeling
Integrated Network Modeling High-throughput experimental technologies have enabled the identification and quantification of biological components at unprecedented scale, from genes and proteins to cells and tissues. Collectively, these technologies provide a parts list for biological systems. Computational systems biology employs an integrative approach to characterize biological systems, in which interactions among all components in a system are described mathematically to establish a computable model that cohesively integrates data. For multiple…
-

100K Wellness Project
The sequencing of the human genome promised to revolutionize diagnosis and treatment of disease. This revolution had as its ultimate goal personalized and predictive medicine, in which treatment is tailored to each individual patient as informed by his or her own unique genome sequence. More recently the precision and cost-effectiveness of additional ‘omic technologies, such as metabolomics and proteomics, have increased dramatically, and their potential to personalized medicine has become…
-
Systems Biology of the Human Microbiome
Microbial species interact with one another to create complex communities, the form and function of which have great environmental, industrial, and health impact. These communities and their environments are referred to as the microbiome – microscopic ecosystems present across the globe, extreme environments barely capable of supporting life, and even within host organisms including humans. Examples of these communities are responsible for nutrient cycling, bioremediation of contaminated sites, and assisting…
-

A Systems Biology Approach to Preterm Birth
Pregnancy complications are an important health concern in both developing and developed countries. Globally, up to 10% of pregnancies result in preterm birth, and high-risk pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia occur in 3-5% of all pregnancies. Preterm birth is the leading cause of newborn death worldwide, and pregnancy complications have long-term implications for the newborns health and wellness. Infants from high-risk pregnancies are more likely to have health issues throughout their lifetimes, as well as long term intellectual and developmental disabilities. The underlying biology regulating the fetal environment and how this environment contributes to complications during pregnancy remain unclear. There is a clinical need to identify biomarkers that may be predictive of preterm birth and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
-
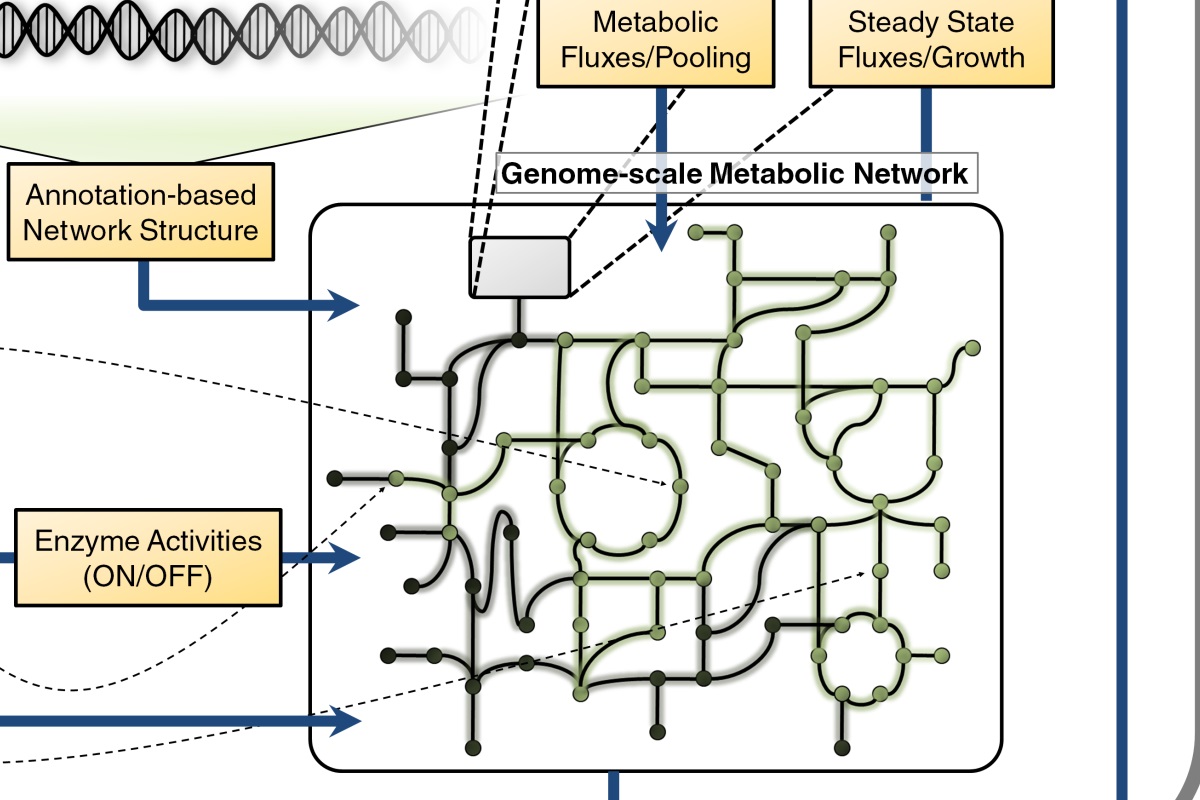
Clostridium beijerinckii reconstruction
Clostritidium beijerinckii is an attractive organism for biofuel production because it can naturally produce high yields of butanol from sugars. In order to better understand this process, we have constructed the first genome scale metabolic model of C. beijerinckii. This model serves as a platform to generate hypotheses for how to metabolically engineer new strains with improved butanol production. Paper in BMC Systems Biology
-
MediaDB
MediaDB collects chemically defined growth media from primary literature sources for fully sequenced organisms. The Price Lab maintains this database, which places emphasis on organisms with existing genome scale metabolic models. We intend for this database to serve as an aid in understanding and designing media, as well as a tool for discovering connections between media compounds and organism characteristics encoded in the genome. MediaDB can be found at https://mediadb.systemsbiology.net/
-

Methanosarcina barkeri reconstruction
Updated Methanosarcina barkeri reconstruction In collaboration with Bill Metcalf’s lab at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, we are sequencing 20 novel Methanosarcina strains. The genomes are being analyzed to learn more about the evolution of metabolic and regulatory networks to identify environmental patterns in their evolution. As part of this analysis, we have updated the genome scale metabolic model of Methanosarcina barkeri Fusaro, a model archaeon. Along with our model of M. acetivorans, this updated model serves…
-
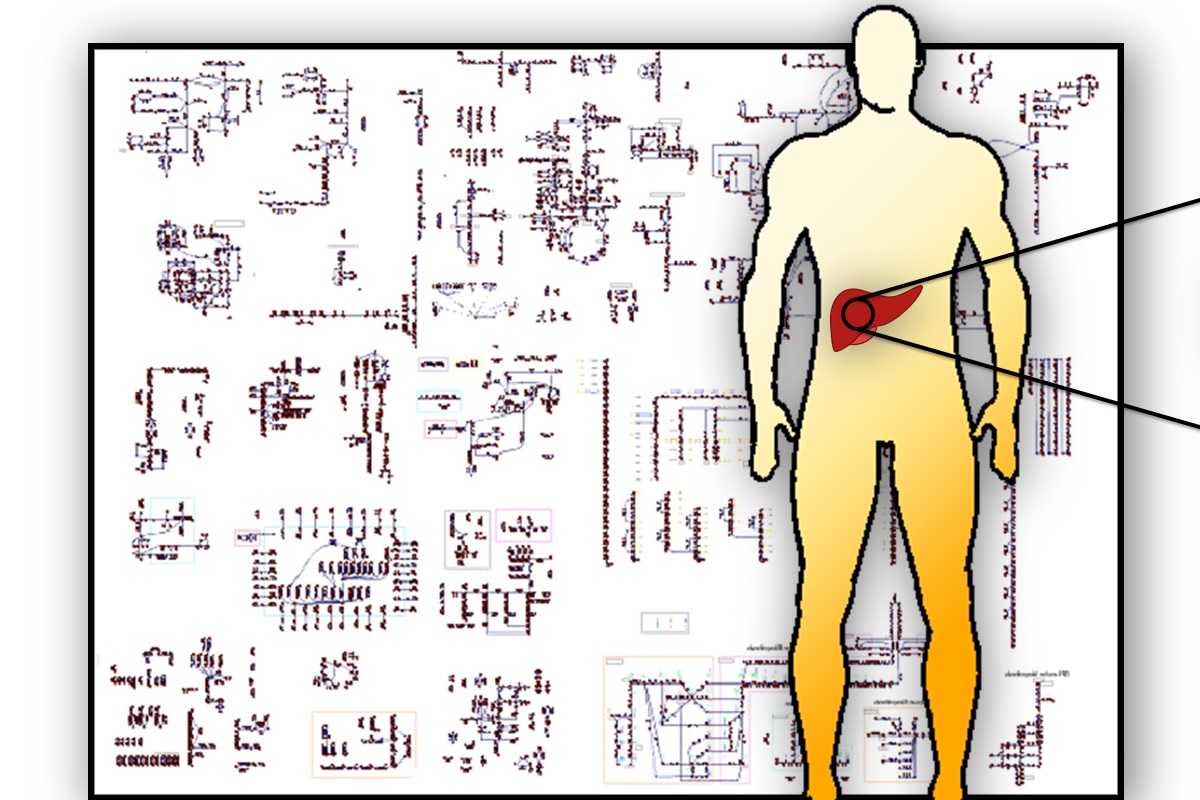
Tissue Specific Encyclopedia of Metabolism (TSEM)
The Price lab is building cell- and tissue-specific metabolic models based on transcriptomic data using our recently developed method – metabolic Context-specificity Assessed by Deterministic Reaction Evaluation (mCADRE). The key innovation of the mCADRE method is to use gene expression data and metabolic network structure to deterministically rank each reaction from a generic human metabolic map in terms of its importance in a tissue-specific metabolic context. We have used mCADRE…
-

Methanosarcina acetivorans reconstruction
Methanosarcina acetivorans reconstruction In collaboration with Bill Metcalf’s lab at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, we are sequencing 20 novel Methanosarcina strains. The genomes are being analyzed to learn more about the evolution of metabolic and regulatory networks to identify environmental patterns in their evolution. As part of this analysis, we have constructed a genome scale metabolic model of Methanosarcina acetivorans C2A, a model archaeon. Along with our updated model of M. barkeri, this…
-

Measuring the effect of inter-study variability on estimating prediction error
We have assessed the influence of technical and biological sources of variability in transcriptomic data on predictive performance of molecular signatures learned from these data. Our approach compares two types of validation methods: (1) ordinary randomized validation (RCV), which extracts random subsets of sample data for testing, and (2) inter-study validation (ISV), which excludes an entire study for testing. Whereas RCV operates based on the assumption of training and testing…
-

ITEP: Integrated Toolkit for Exploration of Pan-genomes
ITEP, the Integrated Toolkit for Exploration of microbial Pan-genomes, is a suite of scripts and Python libraries for the comparison of microbial genomes. It includes tools for de novo protein family prediction by clustering, ortholog detection, analysis of functional domains, identification of core and variable genes and gene regions, sequence alignments and tree generation, cluster curation, and the integration of cross-genome analysis and metabolic networks for study of metabolic network…
-

ISSAC: Identification of Structured Signatures and Classifiers
ISSAC is a multiclass classification tool that can learn molecular signatures from high throughput gene expression data. ISSAC constructs a framework for disease diagnosis: a tree-structured hierarchy of the disease phenotypes under consideration based on agglomerative clustering, and learns panels of binary classifiers corresponding to the nodes and edges of the diagnostic hierarchy. Node classifiers distinguish the phenotype or group of phenotypes apart from all other phenotypes, and edge classifiers…
-
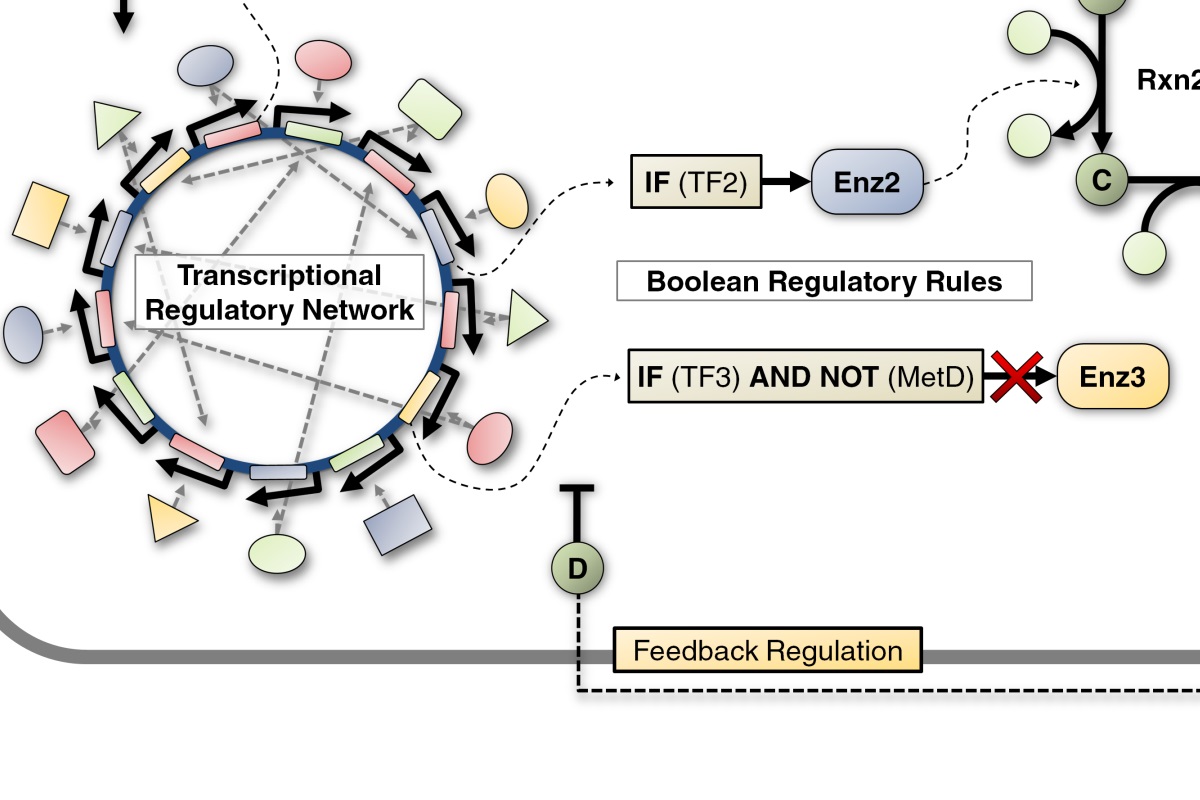
Honeybee Transcriptional Regulatory Network
This was a collaborative project between our lab and Dr. Gene Robinson’s behavioral neuroscience lab and involves the application of systems approaches to predict the effect of a dynamic process like behavior on gene expression. Using a brain transcriptome data set (generated in Dr. Robinson’s lab) unparalleled in size and scope (over 800 individual honeybees sampled in almost 50 behavioral states) we succeeded in reconstructing a Transcriptional Regulatory Network (TRN)…
-

Genetic Co-Occurrence Network across Sequenced Microbes
We have developed a new phylogenetic approach and used it to identify co-occurrence patterns of orthologous genes across all sequenced microbes (at the time). This approach identifies “correlogs” that co-occur in genomes much more often than would be expected by their relative frequencies, suggesting a functional relationship. Data and Software File(s): Correlog_TableS3.xlsx
-
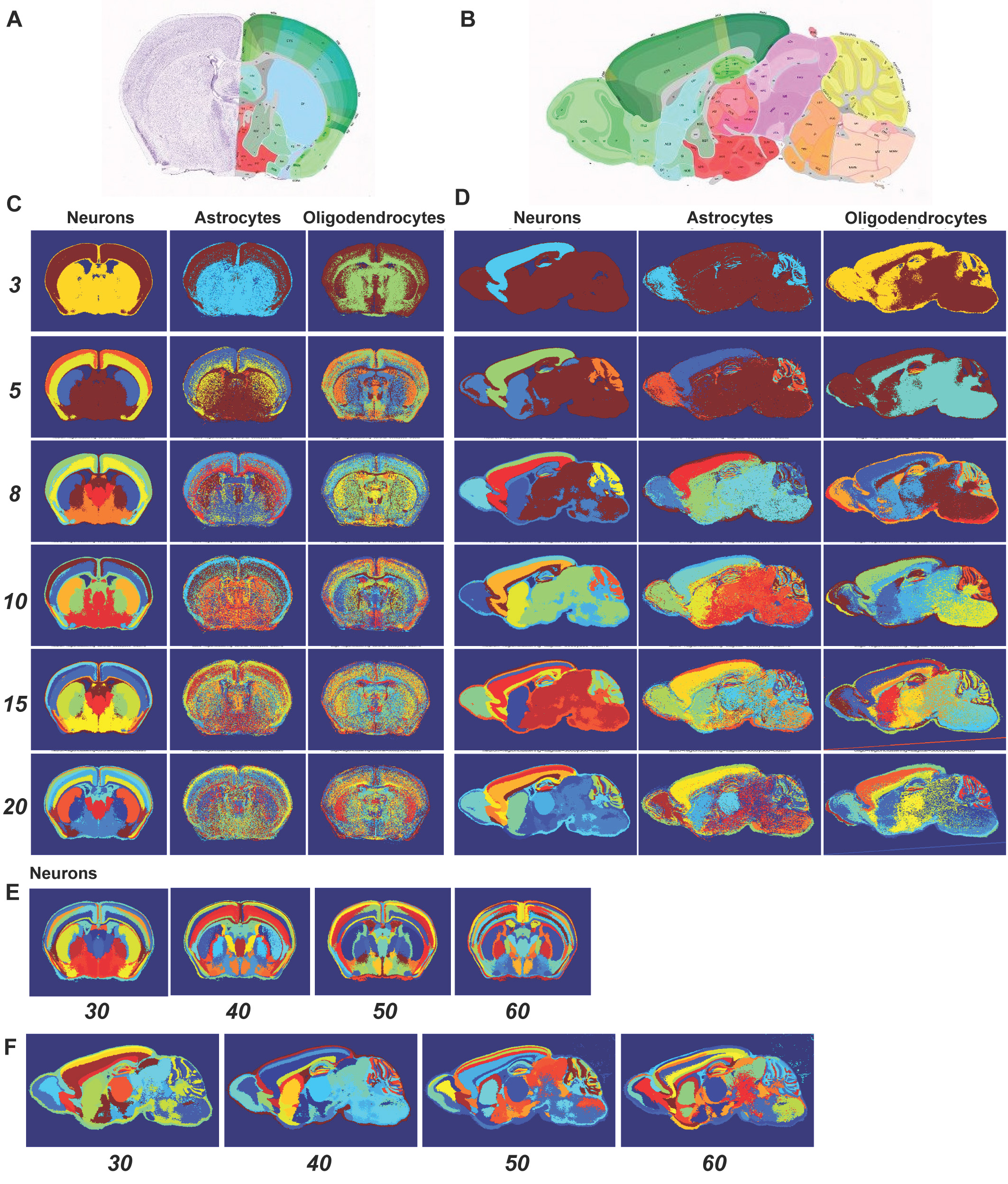
Patterns of spatial expression in the mouse brain
Spatial expression patterns of neuron-specific genes in the adult mouse brain show remarkably clear, spatially-contiguous, transcriptionally-distinct clusters. Over the past year, we have been quantifying the relationships between these spatial expression patterns and known brain regions. To do this, we are taking advantage of a newly released API from the Allen Institute that makes available for the first time three-dimensional grids for the expression of 20,000 genes in 200um^3 voxels of…
-

SNAPR: a bioinformatics pipeline for efficient and accurate RNA-seq alignment and analysis
The growth of next-generation sequencing data now exceeds the growth rate of storage capacity. Researchers’ ability to analyze these data depends upon bioinformatics tools that are fast, accurate, and easy to use. We present SNAPR, a new RNA-seq analysis pipeline designed to handle datasets from a few up to thousands of libraries, while maintaining high alignment accuracy. SNAPR can natively read from and write to BAM format, automatically generate read…
-

Probabilistic Regulation of Metabolism (PROM)
Transcriptional regulation plays a key role in controlling metabolism and a forefront challenge in modeling organisms today is to build integrated models of regulation and metabolism. Predicting the effect of transcriptional perturbations on the metabolic network can lead to accurate predictions on how genetic mutations and perturbations are translated into flux responses at the metabolic level. The Probabilistic Regulation of Metabolism (PROM) algorithm that we developed represents the successful integration…
-

GEMINI: Gene Expression and Metabolism Integrated for Network Inference
There is a strong need for computational frameworks that integrate different biological processes and data-types to unravel cellular regulation. Current efforts to reconstruct transcriptional regulatory networks (TRNs) focus primarily on proximal data such as gene co-expression and transcription factor (TF) binding. While such approaches enable rapid reconstruction of TRNs, the overwhelming combinatorics of possible networks limits identification of mechanistic regulatory interactions. Utilizing growth phenotypes and systems-level constraints to inform regulatory…
-
Microbial Systems Biology
Genome-scale models of microorganisms We are interested in driving forward programs related to model-guided cellular engineering efforts. Genome-scale models provide a powerful resource to guide rational engineering of biological systems for applications in industrial and medical biotechnology. An accurate genome-scale moedle can help predict the systems wide effects of genetic and environemental perturbations on an organisms, and hence drive metabolic engineering or therapeurtic target identification experiments. We apply these approaches…
-

Genome-scale Metabolic Modeling
Microbial metabolic models The primary research goal of this project is to pioneer a systems biology approach to build and utilize a predictable-genome scale model for the lesser-characterized organism C. beijerinckii in order to enhance butanol production for use as a chemical feedstock and a second-generation biofuel. Specific goals include: (1) reconstruct and experimentally validate the first computable genome-scale metabolic network of Clostridium beijerinckii; (2) generate and integrate metabolomics data to enhance the…
-

Brain Structure and Function
Molecular differences between brain regions We have shown that spatial expression patterns of neuron-specific genes in the adult mouse brain show remarkably clear, spatially contiguous, transcriptionally distinct clusters. Specifically, taking advantage of spatial expression data from the Allen Institute, we have applied clustering approaches to reveal that the expression patterns of 170 neuron-specific transcripts revealed strikingly clear and symmetrical signatures for most of the brain’s major subdivisions in the mouse…
-

Human and Mouse Systems Biology
Systems Biology and Disease The systems biology approach to study, diagnose, and treat human disease has become a critical and necessary method to combat the disease’s complex nature. High-throughput experimental technologies have enabled the identification of biological components at unprecedented scale, from cells and tissues to genes and proteins. Collectively, these technologies provide a “parts list” for biological systems (e.g., biochemical pathways, larger interaction networks). Systems biology employs an integrative…
-

Top-scoring ‘N’ algorithm
We have developed a new general formulation of the relative expression algorithm that is geared towards classification using small numbers of measured features (e.g. microRNAs). This is called the top-scoring ‘N’ algorithm (TSN), and it uses a flexible classifier size to expand the permutation and combination space available for classification. TSN relies on an unusual number system known as factoradics to easily translate between permutations of features and decimal numbers….
-

Differential Rank Conservation (DIRAC)
Differential Rank Conservation (DIRAC) is a novel approach for studying gene expression within pathways; this method belongs to a larger family of algorithms designed to identify relative expression (i.e., the ordering among expression values) signatures for diagnosis and prognosis4. Specifically, DIRAC provides quantitative measures of how network ordering differs within and between phenotypes. In the pilot study, we examined disease phenotypes including cancer subtypes and neurological disorders, and we…
-
Gene Editing
Gene editing tools such as CRISPR/Cas9 are employed by the Price Lab to further validate and characterize the transcriptional regulatory architecture of the genome.
-

AUREA: an open-source software system for accurate and user-friendly identification of relative expression molecular signatures
Relative Expression Analysis, which is based on the relative ordering of expression values for a small number of genes, has been shown in several studies to accurately classify between disease phenotypes, cancer subclasses, disease outcomes and diverse human pathologies assayed through blood-borne leukocytes The TSP family of Relative Expression Analysis algorithms possess similar accuracy in classification tasks to other supervised learning based classifiers such as Support Vector Machines; but they…
-

Top-Scoring Pair and Top-Scoring Triple on the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
We have implemented the relative expression classification algorithms the top-scoring pair (TSP) and top-scoring triplet (TST) for the graphics processing unit (GPU). The GPU is a specialized hardware most commonly associated with gaming applications. However, with the NVIDIA’s release of the Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA), the GPU became a general-purpose computational device now widely used in computational biology. The GPU architecture emphasizes massive parallelism, in which thousands of parallel…
-
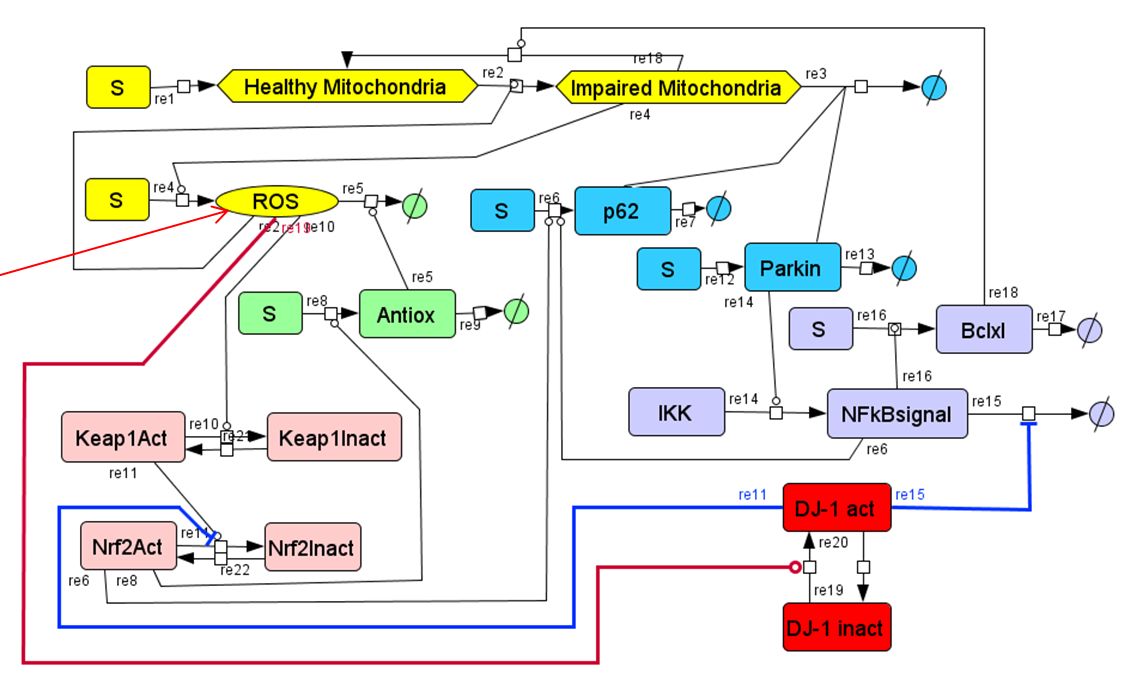
Dynamic Network Modeling
Kinetic modeling of Parkinson’s Disease In Parkinson’s disease (PD), the activities of several components of the reactive oxygen species (ROS)-activated regulatory network are altered. This makes the cell susceptible to ROS damage. In the case of dopaminergic neurons, this effect can be particularly severe. In order to understand the functioning of the ROS-activated regulatory network in normal function and disease, we have built a kinetic model using bottom-up mechanism-based ODE…
-
Understanding the genetic architecture of Bipolar Disorder
3 Bullets Bipolar disorder (BD) is a common, severe and recurrent psychiatric disorder with no known cure and substantial morbidity and mortality. Heritable causes contribute up to 80 percent of lifetime risk for BD. Scientists hope that identifying the specific genes involved in risk for bipolar disorder will lead to new ways to treat the disease. ISB researchers identified contributions of rare variants to BD by sequencing the genomes of…



